Both as a web designer, and as a user of the internet, you know that a fast website is a good websiteSpeed of a website is something which you don’t notice, until it’s missing that is.
Then it becomes frustrating. A bad user experience. A reason for bouncing off a website never to return.
If you want visitors to enjoy their experience on your website, you don’t need to think only about the design of the website, but how fast the website performs for ALL of your users!
Because good design is only one part of a good user experience.
After website design, the speed of page-loading is one of the most important factors which contribute to the success of a website. Besides that, it’s also a ranking factor.
Why is speed so important?
The necessity of having a fast website is a factor has been studied time and time again.
A negative experience is created in the mind of the user who is perceiving a site as being slow. A site’s conversion rate is also affected very negatively by slow performing websites.
Have a look at the graph below by research firm Soasta

Loading time vs conversion rate study
As can be clearly seen from the graph above, as load time of a page increases, the conversion rate drops drastically. The best conversion rates actually happen when pages take less than 3 seconds to load. Unfortunately, very few websites are actually able to provide such a fast user experience.
Is your website one of these slow-loading sites? Are you killing conversions and are not even aware of it?
But there are solutions which can help boost your website’s speed.
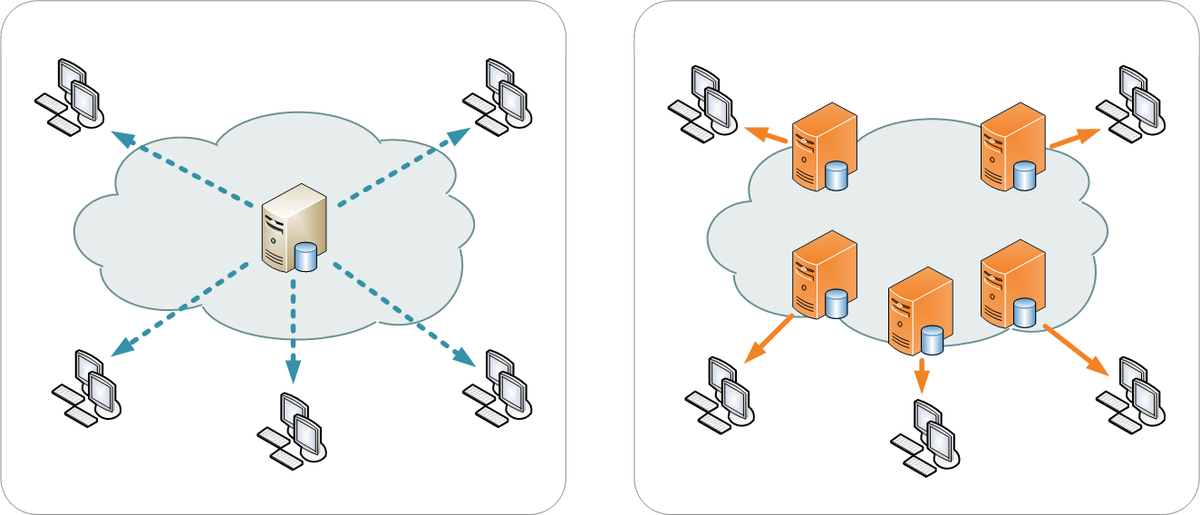
What is a CDN?
The term CDN is an acronym which means content delivery network. That is a fancy way of saying, a network of servers which are optimized to deliver the content (of your website) in the most optimal way.
But how does this content delivery network provide benefits to my website and how does it make the website load faster?
The CDN’s network of servers is an infrastructure which is designed to handle the load of traffic of a website better than that of generic hosting services.
Most hosting services, especially the ones aimed at generic websites are geared at creating a stable but generic environment, at a low cost to both the hosting service and the client. These websites typically run on generic environments, such as Apache, PHP, MySQL and other stacks of popular hosting frameworks.
However, the environment has not been specifically optimized and tuned for website speed. Shared hosting services are typically quite slow, particularly in their initial response. The fact that each environment is hosting multiple websites simultaneously means that they suffer from a resource bottleneck problem. Essentially, each website is hosted on the same server as many others, they are “sharing” the same resources. But while the term used is sharing, in reality, they are competing for the same resources. To keep costs low, this sharing creates a situation where each request sent to a website has to wait before it can be served. (Incidentally, if you are looking for a good share host, check out this review of Inmotion hosting – we really don’t complain much here)
Have a look at the below. One of my websites, which is aimed primarily for ecommerce (dronesbuy.net) is hosted on a shared hosting environment, without a CDN.
Have a look at the following waterfall graph:

Load time without CDN
Can you see the waiting time above of 1.26 seconds?
This is the time it is taking for the server to start “working” on the request sent to it. Essentially, at this point, my website is queued up, competing for resources with other sites hosted on the same server as mine.
This is an implicit delay in created by using a shared website hosting service
Bear in mind, that this delay is before the server event starts to send any kind of content back to the user.
With a delay of 1.26 seconds, you can forget having a page-speed load time of less than 3 seconds.
This is a problem. So how do we go about solving this problem?
On the other hand, a CDN’s primary function is to make websites load fast. Their actual infrastructure setup is designed such that they help deliver a lightning fast website.
But how does a CDN actually speed up my site?
How a CDN speeds up your site
There are a few reasons why a website can load slowly:
- the shared hosting server has a lot of websites (to keep the price cheap) and is thus overwhelmed. The response times are therefore slow.
- Images and other large content of the are not optimized and take a lot of time to download.
- The website has installed many different WordPress plugins which are generating many CSS and JS files and other resources
- The hosting server is located geographically far away from the actual visitors of your website (think website hosted in the US, with readers mostly in Europe)
There are other reasons, but these are the main ones which generate the largest loading time hits.
You can take mitigating steps to fix each of the above-noted problems individually, but we’ll focus mostly on the last two in this article.
Your shared hosting is overwhelmed and slow
Shared hosting servers are by their definition – slow, especially if they are cheap. It’s just the economics of it.
When a hosting company rents or buys a server, they need to share that cost with their clients.
Put simply, and for the sake of example, if your server costs $100/month and you want to price your plan at $10/month, you need to host 10 accounts to break even.
If you want to price your plan at $5/month, you need to host 20 accounts to break even.
You get the gist. The cheaper the plan, the more the accounts you’ll need to host on the same server.
If a hosting service is advertising itself as cheap, and you want your website to be fast – run a mile!
So what happens, on shared servers, each time somebody visits your website, the server is (at the same time) handling the websites of all of the other users / accounts on that same server.
With shared hosting, it can take more than a whole second to even start working on delivering your website’s contents.
You can clearly see that delay on the screenshot above.

VPS vs Shared hosting environment
If you want to make a website fast, this delay of one second in response time is creating a serious issue for you.
Here are our first recommendations
- If your website is using WordPress as the CMS, choose from the best WordPress hosting companies, the ones with known good service and great reviews. Stay away from cheap hosts.
- Going for the highest plan you can afford, a Virtual Private Server is a good balance between a (cheap but slow) shared hosting site and a dedicated server (fast but expensive). With a VPS, your site will have plenty of resources to deal with the load and respond within a few milliseconds, rather than a whole second.
The images of your site are not optimized
Images are one of the primary reasons why websites can be slow to load.
It’s always great advice to use images in your articles. They help to create a break in large pieces of text. Images are also great for readability.
“An image is worth a thousand words” or so they say.
But images can also create problems.
Primarily, images which are not optimized for speed can have a serious negative effect on the loading time of a website.
It’s actually quite a laborious process to remember to save each file in a speed-friendly format, and compressing them to a size which is small enough but which does not lose any of the quality of the image.
Besides being labor-intensive, some people are simply not aware of the need to optimize images.
So what’s the solution to this problem? We need to find a method which will automatically optimize images.
Here’s where a CDN comes to the rescue. CDNs are designed to address this problem without requiring any manual intervention
This is because image optimization (including lossless compression) is typically a built-in feature of most CDNs
That means you don’t have to worry about the images. While you handle the design and creation of a website with awesome imagery, the Content Delivery Network will automatically compress and optimize the images.
The website is using a lot of scripts
This is another factor which has a bad effect on the speed of a website.
Almost all plugins which are installed on a website have an impact on the loading time of your website – each plugin adds more and more assets to the site, making it slower and slower.
Each plugin which is used to create a specific piece of functionality is also slowing down the site.
Some plugins create more JS files, CSS files, and other assets, so some are worse than others, but all of them have at least a bit of an effect. The fewer plugins you install – the better. This is a golden rule.
Each plugin also adds overhead in the form of requests.
Have a look at the following screenshot from a site which has not been optimized for speed. You can see that the performance scores are very slow, whilst the fully loaded time is horrendous.

Slow loading time due to many requests
Thankfully, there are ways to mitigate these problems:
- Install as little plugins as possible on any website
- Combine the files created by all the plugins into a few files only
- Enable HTTPS and then HTTP/2 on your website for better overall loading times
Once again, a CDN can help with the combining the files into fewer files and delivering that content over HTTP2.
The CDN actually performs compression and minification of JS and CSS files; this makes the overall size of your site’s resources smaller and therefore, faster to load.
Setting up of HTTP/2 in also highly recommended. HTTP2 is something which is a whole topic of its own so we’ll recommend a couple of great articles on WebDesignerDepot and on CollectiveRay blog which we’ve already written.
HTTP/2 has been created specifically to make improvements in the loading time of websites. It is designed to address certain shortcomings which older technologies did not deal with.
CDN services typically can enable HTTP/2 on your website, simply through the flick of a switch. HTTP/2 requires that HTTPS has been enabled on your site. Once again, CDNs typically have built-in support to serve content over HTTPS. Thanks to the CDN, you can enable HTTPS without incurring the cost and complication which is associated with secure website certificates. A CDN is also able to improve the overhead associated with the SSL/TLS handshake (which is a heavy operation). This ensures that even with HTTPS enabled – the site incurs no overhead.
There’s still one problem which we haven’t addressed which can slow down the loading speed of your website.
What is it and how can we fix it?
The geographical location of your website server
There is one thing which can negatively your website’s loading speed, even after you’ve performed all sorts of speed optimizations mentioned above.
Have a look at the following diagram.

Hosting server location vs visitor location
This shows the typical time it takes for web data to travel from the one side of the Atlantic to the other. You can see that loading a website hosted on a different continent that your website is visiting from, is a problem. If your website is hosted in the continental US, any visitor outside of the US will experience this problem.
Of course, this applies all over the world. It can even happen within continents if the visitor is located far away from the hosting server.
The distance your website’s content has to travel has a direct (and negative) effect on how fast your website loads.
If your website has a localized audience, choose a good hosting service which is physically close to your target audience. If you are targeting users in New York, choose to host your website on a good server in New York.
However, what do you do if your website caters to an international audience?
You can’t choose a server which is located close to the visitors of your website.
However, there is a solution. As you might have guessed, the solution involves a CDN, because a CDN service specifically addresses this problem.
Let’s see an updated version of the previous diagram, this time we see how the loading time is affected if we use the services of a CDN such as Incapsula CDN, one of the largest players in the CDN industry.

Without CDN vs with CDN
Just like we discussed at the beginning of this article, a CDN service is designed to shorten the distance that content has to travel to reach the visitors of a website.
A CDN service is set up by creating a network of hundreds of servers in different locations in multiple countries and geographies. These servers, known as caching servers or edge servers, each contain a local copy of the images and files which your website needs serve.
When a user accesses your website, these files are served from the nearest physical to your visitor.
This reduces the problem of distance and makes a website much faster to load compared to if a website was not using a CDN.
Have a look the following diagram, which shows the geographical distribution of caching servers around the world – making it possible to always serve content from a location which is physically close to your visitor.

CDN global server map
How to set up a CDN for free
The great thing about CDN services is that they operate on a freemium model – typically they offer a free plan. This free plan provides the localized caching functionality we have shown above.
If your website grows beyond the limits of the free plan, you can then move to a higher plan which suits the needs of your website better.
The easiest way to implement a CDN does not even need a plugin, it’s done by what is knows as a reverse proxy.
This only requires you to perform some changes to the DNS settings of your domain. You’ll find exact guidance for most hosts from the CDN you will opt for, or you can ask for support from the CDN’s support staff.
You can see below how your website together will work together with the CDN to send content to visitors. The origin server is your website’s server.

CDN setup using proxy server
The CDN server actually receives the hit when a user visits your website. It then sends the request to your site, such that any necessary dynamic content is generated. Once it gets a response, the CDN sends the dynamic content and all static resources to the visitor.
This removes a lot of load from your hosting server – making your website load faster and able to handle much more visitors simultaneously.
Conclusion – are you ready to make your website faster?
As we’ve seen in this article, setting up a CDN can start from the very cheap price of free! Besides not having to spend anything, the loading speed of your website will be much-improved giving your site’s visitors a better user experience for your visitors.
If you’re looking to have a fast website, a CDN is a must.





Leave a Reply